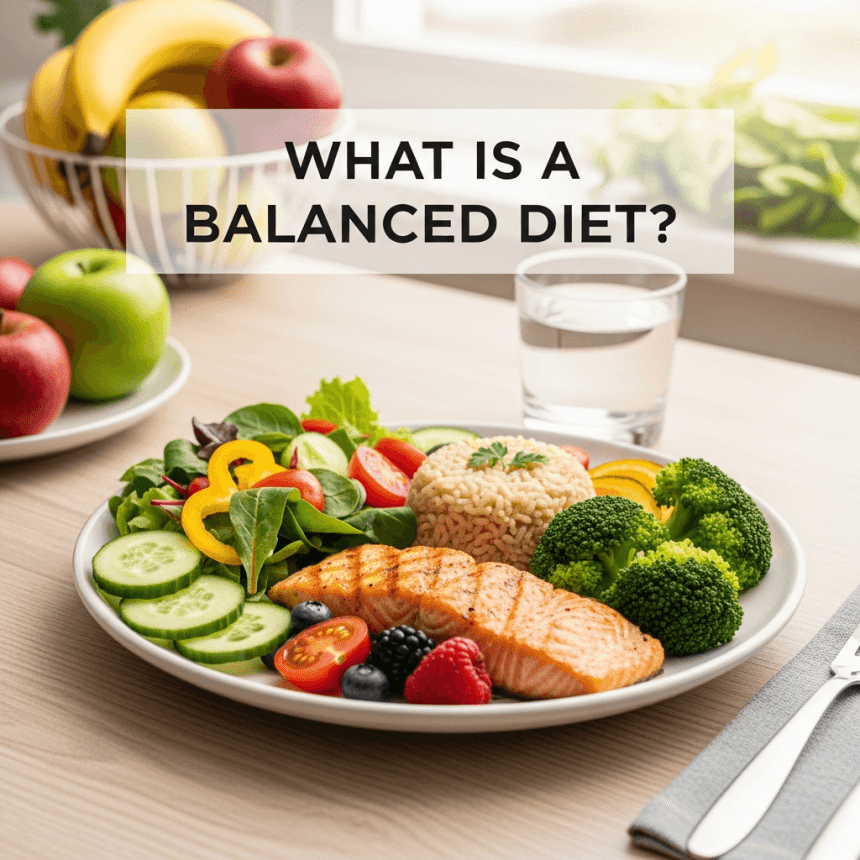In the rapidly evolving landscape of 2026, the concept of a balanced diet has shifted from a rigid set of rules to a personalized, science-backed approach to longevity. For anyone navigating the complexities of modern nutrition, the primary goal remains the same: providing the body with the specific fuel it needs to function at its peak. This guide breaks down the fundamentals of balanced eating in the current year, incorporating the latest health research and official 2025 to 2030 dietary guidelines.
- The Modern Definition of a Balanced Diet in 2026
- The Core Components of Nutrition
- The 2026 Dietary Guidelines: A Shift Toward Real Food
- Food as Medicine: The Rise of Functional Nutrition
- Personalizing Your Diet with 2026 Technology
- The Mediterranean Diet: Still the Gold Standard
- Practical Steps to Achieving a Balanced Diet
- The Link Between Diet and Mental Wellbeing
- Live Daily Information
- Why Balance Matters for the Long Term
The Modern Definition of a Balanced Diet in 2026
At its simplest, a balanced diet is a way of eating that provides all the essential nutrients your body requires to work effectively. Without balanced nutrition, your body is more prone to fatigue, infection, and poor performance. In 2026, the global health community has moved toward a “Food as Medicine” philosophy. This means we no longer just look at calories. We look at how specific foods interact with our biology to prevent chronic conditions and enhance mental clarity.
A balanced diet today focuses on three major pillars:
- Diversity of whole, unprocessed food sources.
- Alignment with metabolic health markers.
- Personalization through real-time data and wearable technology.
The Core Components of Nutrition
To understand a balanced diet, you must understand the building blocks that make up your daily intake. These are divided into macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients: The Big Three
Macronutrients are the nutrients you need in large amounts to provide energy.
High-Quality Proteins
Protein is the primary building block for muscles, skin, and hormones. In 2026, there is a significant emphasis on protein timing and quality. Top sources include lean meats, wild-caught fish, eggs, and plant-based options like lentils and fermented soy. Current guidelines recommend aiming for 1.2 to 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, especially for those prioritizing metabolic resilience.
Healthy Fats
The narrative around fat has changed. We now prioritize “essential” fats that support brain health and hormone production. This includes monounsaturated fats found in extra virgin olive oil and avocados, as well as omega-3 fatty acids from oily fish like salmon and mackerel. Interestingly, the latest 2026 updates from the Department of Health and Human Services suggest that full-fat dairy, when consumed without added sugars, can be a valuable part of a nutrient-dense diet.
Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred energy source. However, the focus has shifted entirely away from refined sugars and toward fiber-rich, whole-food sources. Think of ancient grains like quinoa and millet, as well as starchy vegetables like sweet potatoes. These provide a steady release of glucose, preventing the energy crashes associated with processed flours.
Micronutrients: The Spark Plugs
Micronutrients include vitamins and minerals. While needed in smaller amounts, they are essential for every chemical reaction in your body.
- Vitamins: Essential for immune function (Vitamin C, D) and energy production (B-complex).
- Minerals: Vital for bone health (Calcium, Magnesium) and oxygen transport (Iron).
In 2026, many individuals use personalized blood panels to identify specific micronutrient deficiencies, allowing them to tailor their balanced diet more precisely than ever before.
The 2026 Dietary Guidelines: A Shift Toward Real Food
The latest federal nutrition policy released in January 2026 marks a historic reset. The emphasis is now clearly on “real food” and the dramatic reduction of ultra-processed items.
Key Recommendations for Daily Eating
Prioritize Whole Foods
The current recommendation is that at least 80% of your plate should consist of whole, recognizable foods. This includes fresh produce, raw nuts, and minimally processed proteins. The goal is to avoid hidden additives and synthetic dyes that have been linked to systemic inflammation.
The Half-Plate Rule
A simple way to visualize balance is the “Healthy Eating Plate.” Aim to fill half of your plate with colorful vegetables and fruits. The remaining half should be split equally between high-quality proteins and whole grains or starchy tubers.
Hydration and Sugar Limits
Water remains the gold standard for hydration. Current health trends show a massive move away from sugar-sweetened beverages and even “low-calorie” artificial sweeteners. Most experts now recommend limiting added sugar to less than 10 grams per meal to maintain stable insulin levels.
Food as Medicine: The Rise of Functional Nutrition
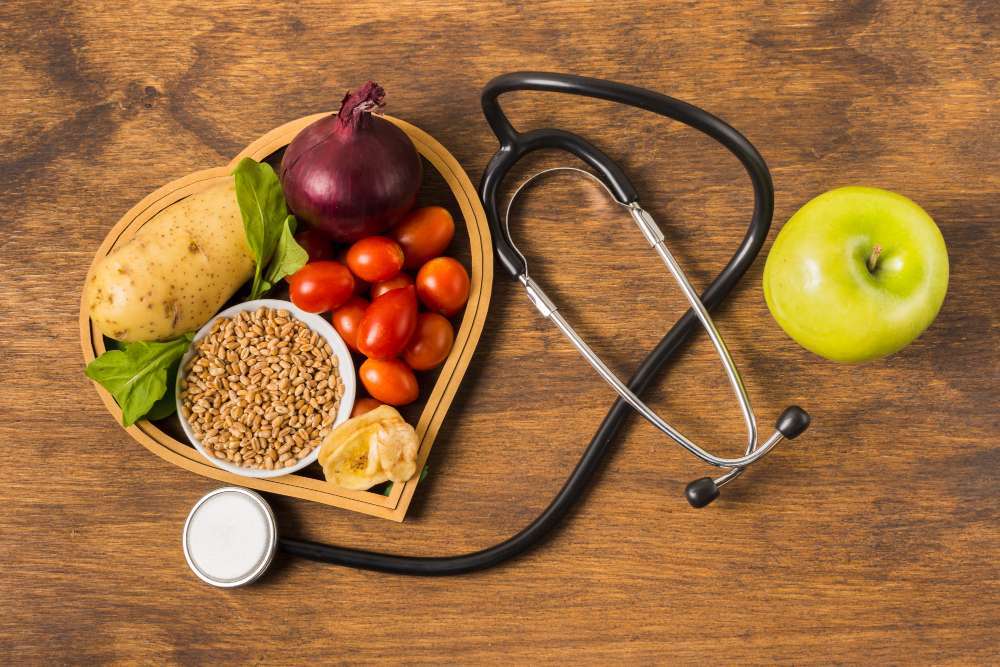

In 2026, the concept of a balanced diet includes functional foods: items that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition.
Gut Health and the Microbiome
We now know that a balanced diet is incomplete without attention to the gut microbiome. Incorporating fermented foods like kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi helps populate the gut with beneficial bacteria. This is directly linked to improved mood, stronger immunity, and better weight management.
Anti-Inflammatory Eating
Chronic inflammation is recognized as a root cause of many modern ailments. A balanced diet in 2026 is naturally anti-inflammatory, rich in antioxidants from berries, dark leafy greens, and spices like turmeric and ginger.
Personalizing Your Diet with 2026 Technology
One of the biggest changes this year is the integration of AI and wearable technology in dietary planning. We are moving past a “one size fits all” model.
Metabolic Feedback
Wearable devices like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are now widely used by non-diabetics to see how different “healthy” foods affect their blood sugar. For instance, some people may find that oatmeal causes a spike, while others thrive on it. This data allows for a truly balanced diet tailored to your unique biology.
AI-Powered Meal Planning
Sophisticated AI tools can now analyze your activity levels, sleep quality, and even your DNA to suggest daily meal plans. This ensures you are getting the exact ratio of nutrients needed for your specific lifestyle, whether you are an elite athlete or a busy professional.
The Mediterranean Diet: Still the Gold Standard
Despite the technological leaps, the Mediterranean diet remains the most scientifically supported eating pattern in 2026. Experts consistently rank it as the top strategy for longevity and heart health.
Core Principles of the Mediterranean Approach:
- High intake of vegetables, fruits, beans, and nuts.
- Daily use of healthy fats, primarily olive oil.
- Moderate portions of dairy, fish, and poultry.
- Very low consumption of red meat and processed sweets.
This pattern is not just a diet but a lifestyle that emphasizes seasonal eating and the social aspect of sharing meals.
Practical Steps to Achieving a Balanced Diet
Transitioning to a balanced diet does not have to be overwhelming. Success is built on small, sustainable habits.
Master the Art of Meal Prepping
Planning your meals in advance is the most effective way to avoid the trap of convenience foods. Spend a few hours on the weekend washing vegetables, cooking grains, and portioning proteins. Having healthy options ready to go makes it much easier to stick to your goals during a busy week.
Learn to Read Labels Like a Pro
In 2026, food labeling has become more transparent, but it is still important to be vigilant. Look for short ingredient lists. If you cannot pronounce most of the items on the label, it is likely ultra-processed and should be avoided. Pay close attention to “hidden” sugars under names like maltodextrin or rice syrup.
Practice Mindful Eating
How you eat is just as important as what you eat. Slowing down and chewing thoroughly allows your brain to receive the “fullness” signals from your stomach, preventing overeating. In 2026, many wellness programs include mindfulness training as a core part of nutritional success.
The Link Between Diet and Mental Wellbeing
Perhaps the most significant realization in recent years is the profound impact of nutrition on mental health. A balanced diet provides the precursors for neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
- Brain Fuel: Complex carbs and healthy fats provide the steady energy your brain needs to focus.
- Mood Regulation: Amino acids from protein are essential for emotional stability.
- Stress Management: Magnesium and B-vitamins found in whole grains and greens help the body manage cortisol levels.
By eating for your brain, you naturally support your body’s physical health as well.
Live Daily Information
As of today, current health data shows a surge in “protein-first” breakfast routines across the globe. Researchers are finding that consuming 30 grams of protein within an hour of waking up significantly improves metabolic rate and reduces cravings later in the day. Additionally, the latest “Whole Lotta Goodness” trend in Europe and North America is encouraging a return to “heritage” vegetables like purple carrots and heirloom tomatoes, which have been found to contain higher concentrations of phytonutrients than standard supermarket varieties.
Why Balance Matters for the Long Term
A balanced diet is not a temporary fix or a “crash” program. It is a lifelong commitment to quality of life. By focusing on nutrient density and avoiding the pitfalls of ultra-processed foods, you are investing in a future with more energy, fewer doctor visits, and a sharper mind.
In summary, a balanced diet in 2026 involves:
- Focusing on whole, real foods as defined by the latest HHS guidelines.
- Prioritizing high-quality proteins and healthy, natural fats.
- Utilizing modern technology to personalize your intake.
- Maintaining gut health through fermented foods and fiber.
- Avoiding refined sugars and artificial additives.